HTTP codes are important elements that inform browser the address to target a webpage or a resource. When the user clicks a link, it is asking the web server for the page that it is linked to. The resulting display with the status code of 200 means that the page was found successfully. There are several HTTP status codes that are used for different files used. They are used on webpage image, CSS Stylesheet, Javascript, web pages, etc.
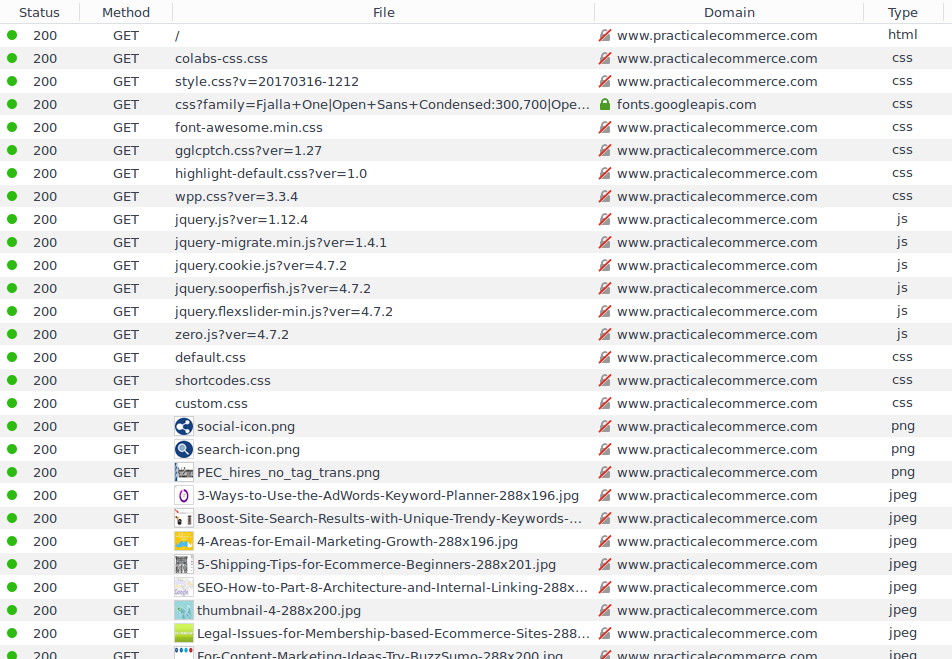
The above is an example of the home page of Practical Ecommerce that shows 200 as the status code that returned 83 times. The common status codes are of significance to all web developers. All of them may be not looking for the same but to recognize an error page 500 instead of redirect 301 is a talent, developer should know. This is typically useful also for the non-developers to be aware of their status codes. Codes are basically the language through which the whole web works so it is highly important to be fluent to be able to understand the store functions. It is also important if the store use or consumes or interacts with an API. HTTP status codes are the switchboards for an API.
HTTP Status Codes
Status Code groups and the Codes within the group are important for an Ecommerce site.
Items in progress – 100 Group
Successful responses – 200 Group
Redirect – 300 Group
Browser errors – 400 Group
Server errors – 500 Group
The above group helps to identify the general status codes even without knowing the exact code. 403 errors would let know that it was an URL related and a 511 would be related to the server.
100 Group – These are rarely used outside the data streaming so kindly ignore 100 group status codes.
200 Group – it is common generic 200 OK responses, which means 200 OK is fully accepted and successfully implemented with no problems.
201 Created (API) means something was created.
204 No Content (API) helps the server to process request but nothing to show.
300 Group – consists of two common redirect responses of 301 and 302.
301 Moved permanently, it means, the browser should use different URL it actually includes a new URL. When the browser gets the code, it opens new redirected URL from the server.
304 Found is a temporary redirect, its function is same as 301. 304 Not modified states that the browser has latest version of URL and it should be using that version. This often commonly happen with caching to speed up repeat views of the page or a file.
400 Group – These are the Client Errors, it includes half of the error codes, 400 group error represents to the client or a browser.
400 Bad Request shows it is a generic error when the browser requested wrong information; there are also specific error codes.
401 Unauthorized (API), it happens when the browser isn’t authorized to use the page. It helps protect private information.
403 Forbidden (API), it is similar to 401 Unauthorized error. The only difference here is 403 error is logged in correctly but lacks permission for access to something.
404 Not Found means the server cannot find any URL.
405 Method Not Allowed (API) – It is a common error with API Development, it usually occurs when HTTP is incorrectly used such as the form trying to send the data to a URL.
429 Too Many Requests (API) – Some APIs limit other APIs in the way it can be used. When it is used too quickly, the error is returned to let know that you have reach the limit.
500 Group is meant for the Server Errors. There are not many of these and they are not generic and 500 Error is common.
500 Internal Server Error shows that there is generic error if something is wrong on the server.
502 Bad Gateway (API), server communicates with other servers if they do not get any response than the code is sent to the browser.
503 Service Unavailable, it is when the server gets overloaded and fails. It will show this message; it means one should try later.
504 Gateway Timeout (API) it is very similar to 502 Bad Gateway, the error is more specific and deals with other server that is not responding at all.